a) Introduction
3.1 Explain the terms homologous series, hydrocarbon, saturated, unsaturated, general formula, and isomerism.
Organic Compound
The compounds of carbon are called organic compounds. However, for conventional reasons, metal carbonates, carbon dioxide, and carbon monoxide are not included in organic compounds.
Examples: Methane ($\text{CH}_4$), Ethanol ($\text{C}_2\text{H}_5\text{OH}$), Carbon Tetrachloride ($\text{CCl}_4$), Benzene ($\text{C}_6\text{H}_6$), etc.
The main branches of organic compounds are:
- Aliphatic hydrocarbons
- Aromatic hydrocarbons
Homologous Series
A homologous series is a family of compounds with the same functional group and general formula, exhibiting similar physical and chemical properties.
Characteristics of Homologous Series
- They have a general formula.
- They differ in molecular formula.
- A homologous series has similar chemical properties.
- Their physical properties follow a trend.
- Each homologous series has a functional group.
- Each member in a homologous series differs in molecular formula from the next by $\text{CH}_2$.
Hydrocarbon
Compounds that are made of only hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons are of two types: Saturated and Unsaturated.
| Saturated | Unsaturated |
|---|---|
| Contain C-C single bond (e.g., Alkanes) | Contain C=C double bond (e.g., Alkenes) |
| Give substitution reactions | Give addition reactions |
| A part of saturated compounds is comparatively less reactive | A part of unsaturated is more reactive than saturated |
| Alkanes do not polymerize | Alkenes can be polymerized |
| Saturated hydrocarbons cannot change the color of bromine water | Unsaturated hydrocarbons can change the color of bromine water |
General Formula
The general formula confirms which compound belongs to which homologous series.
- Alkanes: $C_nH_{2n + 2}$
- Alkenes: $C_nH_{2n}$
- Alcohols: $C_nH_{2n + 1}OH$
- Carboxylic acids: $C_nH_{2n + 1}COOH$
- Amines: $C_nH_{2n + 1}NH_2$
Functional Group
A functional group is an atom or group of atoms that controls the properties of a homologous series.
Isomerism
Molecules with identical molecular formulae but different structural formulae are called isomers.
Example: Isomers of Butane
Types of Formula
| Name | Molecular Formula | Structural Formula | Displayed Formula |
|---|---|---|---|
| Butane | $C_nH_{2n+2}$ | $\text{CH}_3\text{CH}_2\text{CH}_2\text{CH}_3$ | 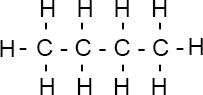 |